



 OJECT
OJECT |
Evaluatie-methoden |
Descriptor |
|
Pareto Analysis |
Pareto analysis is a very simple technique that helps you to choose the most effective changes to make. It uses the Pareto principle - the idea that by doing 20% of work you can generate 80% of the advantage of doing the entire job. Pareto analysis is a formal technique for finding the changes that will give the biggest benefits. It is useful where many possible courses of action are competing for your attention. |
|
Paired Comparison Analysis |
Paired Comparison Analysis helps you to work out the importance of a number of options relative to each other. It is particularly useful where you do not have objective data to base this on. This makes it easy to choose the most important problem to solve, or select the solution that will give you the greatest advantage. Paired Comparison Analysis helps you to set priorities where there are conflicting demands on your resources. |
|
Grid Analysis |
Grid Analysis (also known as Decision Matrix analysis or Pugh Matrix analysis) is a useful technique to use for making a decision. Decision matrices are most effective where you have a number of good alternatives and many factors to take into account. The first step is to list your options and then the factors that are important for making the decision. Lay these out in a table, with options as the row labels, and factors as the column headings. Next work out the relative importance of the factors in your decision. Show these as numbers. We will use these to weight your preferences by the importance of the factor. These values may be obvious. |
|
Cost/Benefit Analysis |
Cost/Benefit Analysis is a relatively simple and widely used technique for deciding whether to make a change. As its name suggests, to use the technique simply add up the value of the benefits of a course of action, and subtract the costs associated with it. Costs are either one-off, or may be ongoing. Benefits are most often received over time. We build this effect of time into our analysis by calculating a payback period. This is the time it takes for the benefits of a change to repay its costs. |
|
Evaluatie-methoden |
Descriptor |
|
Decision Tree Analysis |
Decision
Trees are excellent tools for helping you to choose between several
courses of action. They provide a highly effective structure within
which you can lay out options and investigate the possible outcomes of
choosing those options. They also help you to form a balanced picture of
the risks and rewards associated with each possible course of action.
You start a Decision Tree with a decision that you need to make. Draw a
small square to represent this towards the left of a large piece of
paper. |
|
PMI |
PMI
stands for 'Plus/Minus/Implications'. It is a valuable improvement to
the 'weighing pros and cons' technique used for centuries. |
|
Force Field Analysis |
Force
Field Analysis is a useful technique for looking at all the forces for
and against a decision. In effect, it is a specialized method of
weighing pros and cons. |
|
Six Thinking Hats |
'Six Thinking Hats' is an important and powerful technique. It is used to look at decisions from a number of important perspectives. This forces you to move outside your habitual thinking style, and helps you to get a more rounded view of a situation. |
|
6 Sigma |
|
|
Decision making framework |
|
|
Kepner Tregoe Analysis (Same principle as Grid Analysis |
|
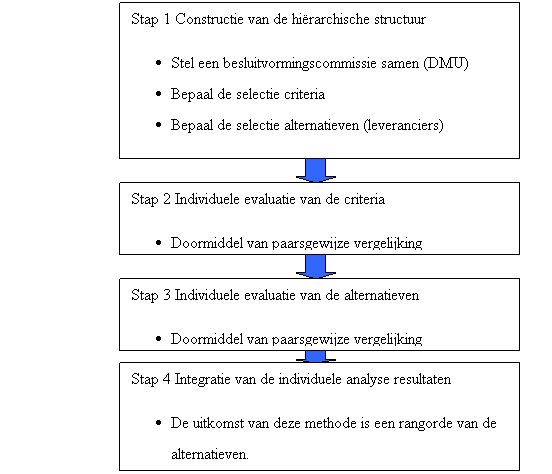
AHP
When you need specific information please send my a e-mail.
18-10-2009